coreboot
The open source coreboot firmware project implements verified boot, which is similar to a combination of OBB verification and UEFI Secure Boot.
Figure 3-2 shows the verified boot flow. Table 3-2 shows keys used in the verified boot flow.
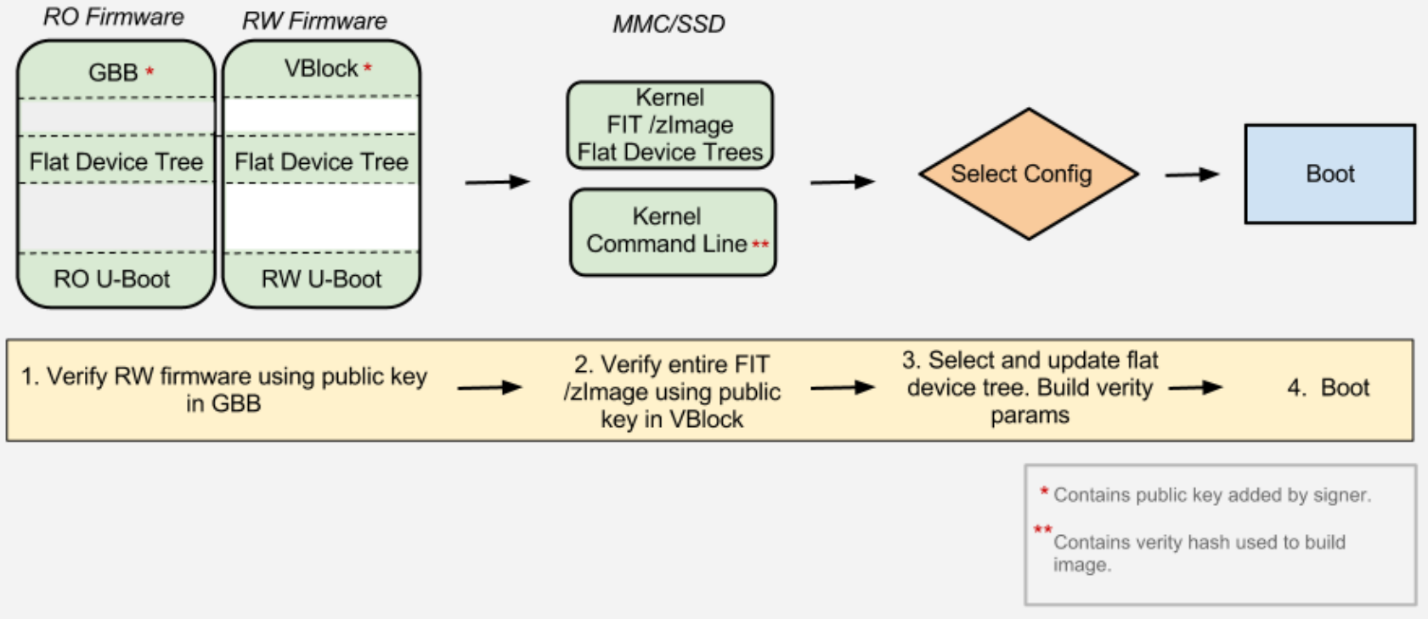
Figure 3-2: coreboot Verified Boot (source: “Verified Boot in Chrome OS and how to make it work for you”)
Table 3-2: Keys used by coreboot verified boot (source: “Verified Boot: Surviving in the Internet of Insecure Things”)
| Key | Verifies | Stored in | Versioned | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root Key | Firmware Data Key | RO Firmware | NO | Private key in a locked room guarded by laser sharks; N of M present. RSA4096+ |
| Firmware Data Key | RW Firmware | RW FW Header | YES | Private key on signing server. RSA4096. |
| Kernel Subkey | Kernel Data Key | RW Firmware | YES (as FW) | Private key only needed to sign new kernel data key. RSA4096. |
| Kernel Data Key | OS Kernel | OS kernel Header | YES | Private key on signing server. RSA2048. |
| Recovery Key | Recovery OS Kernel | RO Firmware | NO | Locked room and laser sharks. RSA4096+. Different than all keys above. Signs recovery installer, not payload. |
Table 3-3: coreboot Verified Boot (for firmware)
| Item | Entity | Provider | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| TP | Read/Write Firmware Verification | OEM | Flash (Read Only Region) |
| CDI | Read-Only Firmware | OEM | Flash (Read Only Region) |
| Root key | OEM | RO firmware, Google Binary Blob (GBB) | |
| UDI | Read/Write Firmware | OEM | Flash (Read Write Region) |
Table 3-4: coreboot Verified Boot (for OS)
| Item | Entity | Provider | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| TP | OS Kernel Verification | OEM | Flash (Read Write Region) |
| CDI | Read-Write Firmware | OEM | Flash (Read Write Region) |
| Kernel Subkey | OSV | R/W firmware, Google Binary Blob (GBB) | |
| UDI | OS Kernel | OSV | External storage |